What is the gig industry?
The gig industry is composed of independent contractors and freelancers instead of full-time employees. It is based on flexible, temporary, or freelance jobs. There are many perks provided by the gig industry – being your own boss, setting your hours, working on projects you’re passionate about, and many more. The gig industry makes work more adaptable to the moment’s needs and demands for a flexible lifestyle. The gig economy also has its downsides due to the erosion of traditional economic relationships between workers, businesses, and clients.
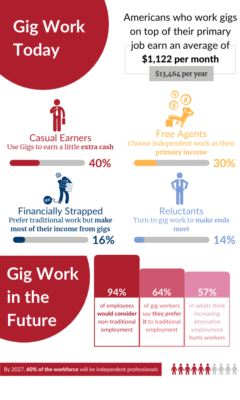
To earn enough money to make a living, gig workers typically take on multiple jobs or gigs at a time. Some do freelance or contract work on the side of their traditional jobs to make extra money or gain skills in another field. While many people turn to the gig industry to make extra money from side jobs, some use it for their primary income. Gig work is the primary source of income for more than one in 10 workers.
What is considered a “gig”?
 "Gig workers are independent contractors or freelancers who typically do short-term work for multiple clients. The work may be project-based, hourly or part-time, and can either be an ongoing contract or a temporary position.” – U.S. Chamber of Commerce
"Gig workers are independent contractors or freelancers who typically do short-term work for multiple clients. The work may be project-based, hourly or part-time, and can either be an ongoing contract or a temporary position.” – U.S. Chamber of Commerce
- Rideshare Drivers
- Food Delivery Drivers
- Pet Sitters
- Freelancers
- Personal Shoppers
- Movers
- Virtual Assistant
- Renter
- So many more!
Is the gig industry dead?
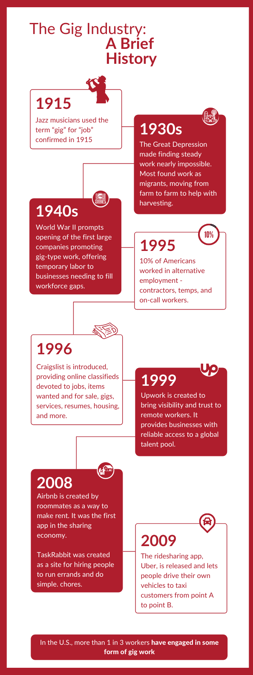
The gig industry is far from dead it has grown significantly in the last two years. As of 2021, gig workers make up over 36% of the U.S. workforce. During the COVID-19 pandemic, even more, workers joined the gig economy, as those who lost their full-time jobs began freelancing to make ends meet. The gig economy experienced significant growth as those whose jobs had been eliminated turned to part-time and contract work for supplemental income. Workers turned to gig jobs in the face of layoffs, office closures, and unstable work environments. Furthermore, the surge in remote work led to people exploring remote contract positions.
As Millennials continue to make up the majority of the workforce, their values shape the economy. Individuals, particularly younger ones, prefer freelancing over full-time employment since it provides them with greater flexibility and independence. Non-traditional work enables them to pick their hours, place of employment, and clients.
Similarly, the gig industry benefits companies as well. Firms may profit from a flexible workforce by spending less money on training and recruitment, not paying for medical coverage, and replacing their staff efficiently if required. It is predicted that by 2027, more than 60% of the workforce will be independent contractors.